|
A cyber risk management-mindset for MSMEs Introduction and background notesClick to read
 The content of this training module is a non-official follow-up to EntreComp for cyber risk-readiness. Back in the previous units we referred several frameworks to be better equipped in assessing and evaluating cyber risks and threats coming from the IT environment. In the following section, we will provide learners conceptual roadmaps to navigate cyber security, cyber readiness and cyber resilience from a quality assurance and risk management perspective.
As a matter of facts, evidences from the aforementioned report indicates that the main causes that intervenes as further disruptors are associated to human factors, rather than technological inefficiencies:
Source: IBM, 2021
Risk Management Click to read
 Evidences gathered by Cyber MSMEs’ partners identify in the lack of reliable (cyber) risk management systems one of the most common cause of cyber exposure. Per se, this result is indicative of the “non-acknowledgement” of cybersecurity as a top-concern for business resilience and competitiveness.
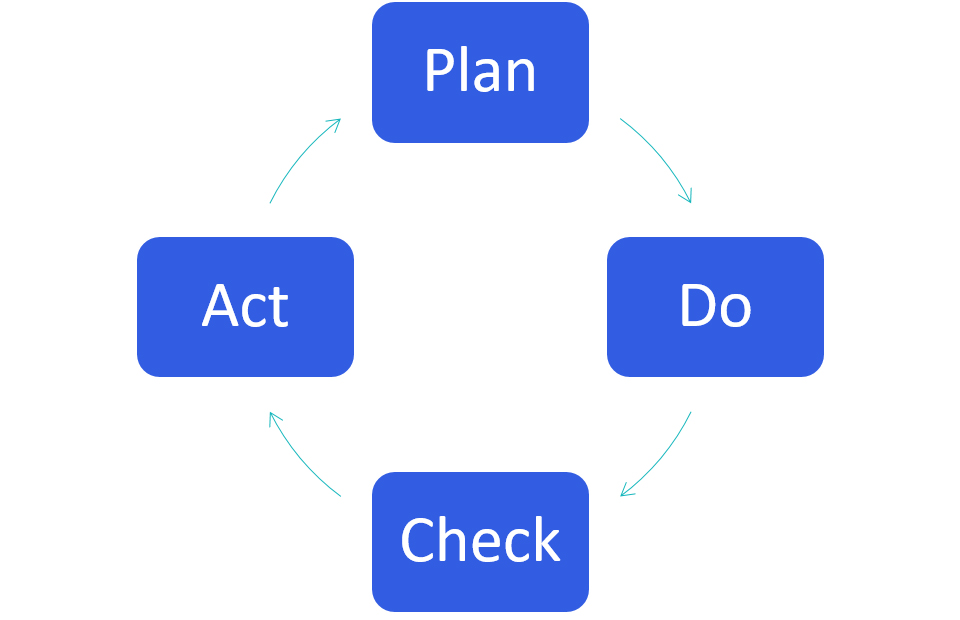
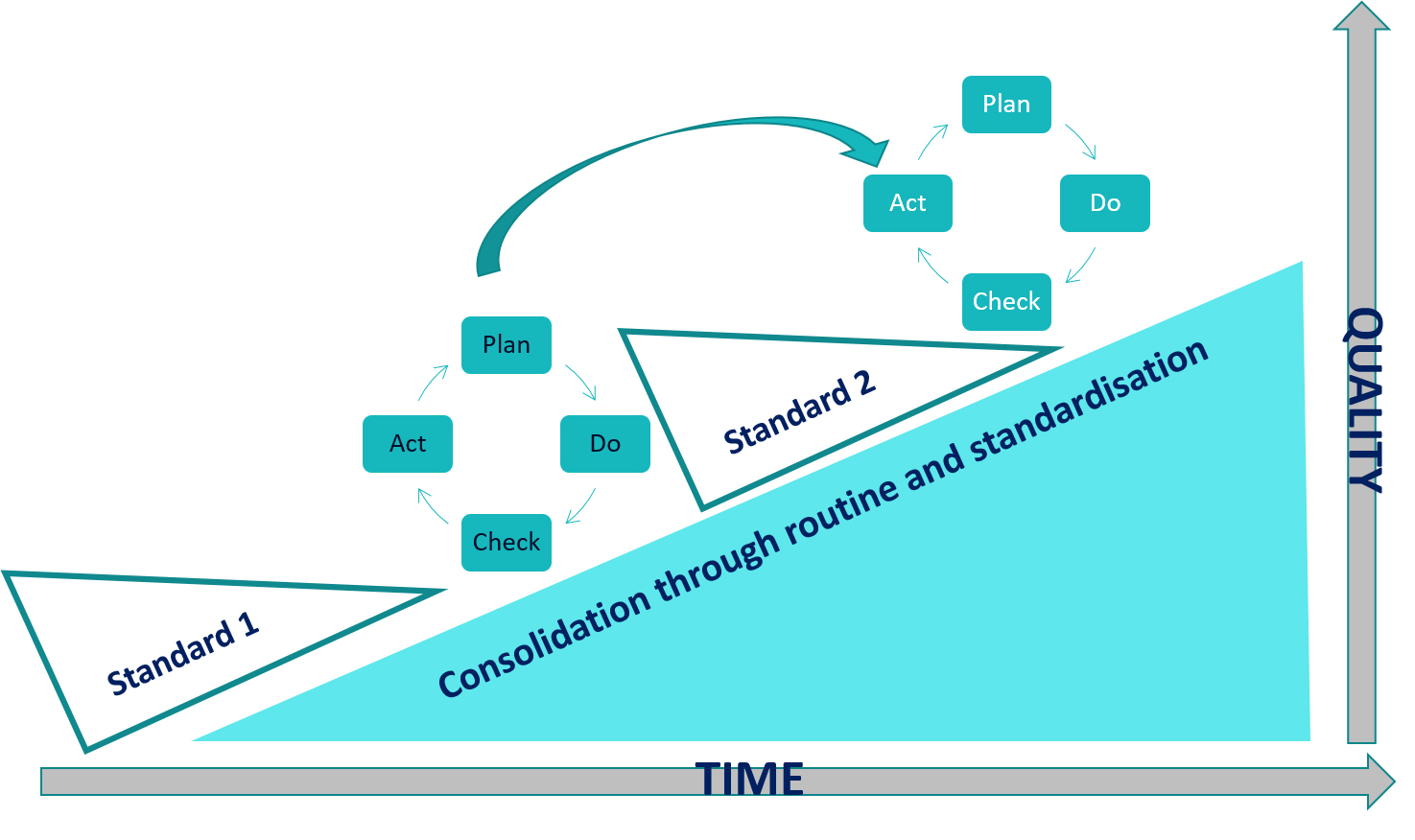
ISO 31000The International Organisation for Standardisation recognise in risk management a process involving the systematic application of policies, procedures and practices to the activities of communication and consulting, establishing the context and assessing, treating, monitoring, reviewing, recording and reporting risk. As all business functions remain bond to the efficiency and effectiveness of IT systems and networks regulating their tasks’ flow, cyber risk management becomes an integral part of strategic decision-making and long-term planning. Cyber risk management is a cyclical process and it includes an on-going mechanisms orientated to the achievement of ever higher standards. Check > Evaluation > Fine-tuning
ISO 31000, a visual representation
Mitigating the cyber riskClick to read
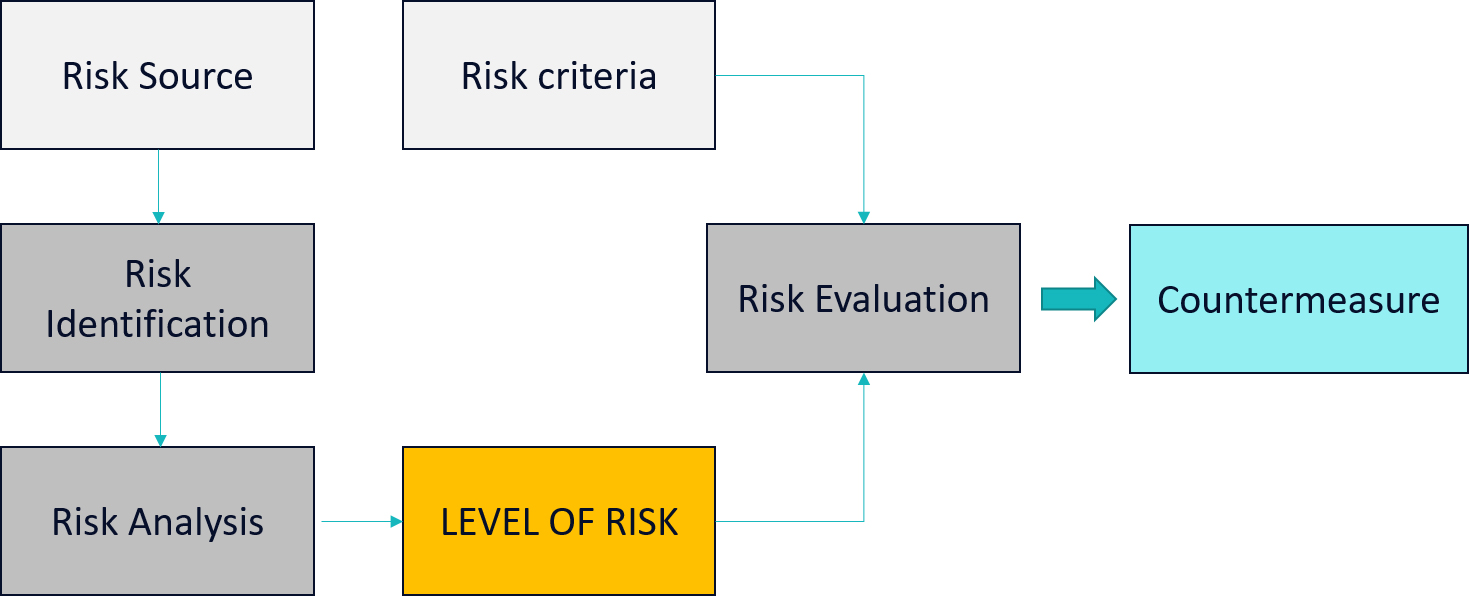
 Based on ISO 31000, internal (cyber) risk management models should reflect the organization’s values, objectives and resources and be consistent with policies and statements about organization’s obligations and the views of stakeholders. Once the organisation settles the scope, context and criterium of its management model, it is recommended to proceed with the actual assessment. The assessment concludes in a three-step process:
The Risk Evaluation FlowClick to read
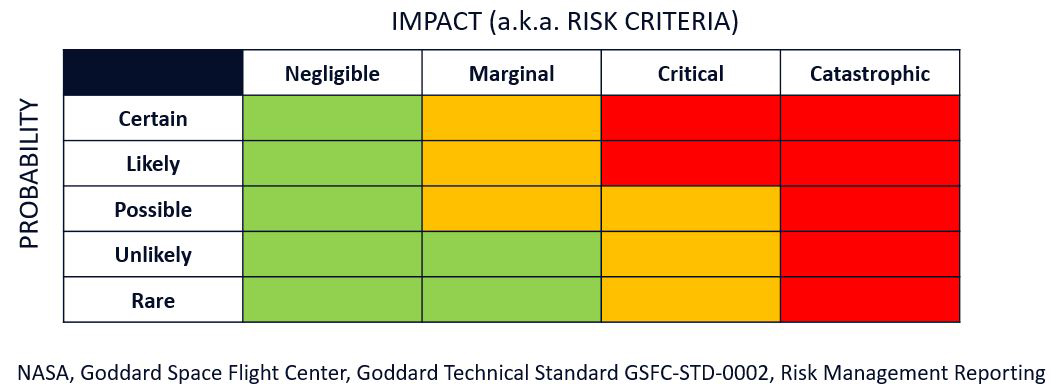
 The Risk Assessment Grid Click to read
 Quality Assurance for cyber-hygiene An introduction to Quality AssuranceClick to read
 Professionals and experts in the domain of business management will certainly have heard of Lean Manufacturing, Total Quality Management (TQM), Just In Time (JIT), etc. The ones that we just mentioned are among the most notorious audit frameworks for quality management applied at industrial level. These models have all one thing in common: their origins are from Japan and they became worldwide the top reference for audit and quality assurance procedures. An introduction to Quality Assurance – KAIZEN Click to read
 What is less known about TQM and JIT, is the business “philosophy” from which they emerged: Kaizen (改善), literally translated as 改 = change,善 = good. Kaizen’s culture implies a constant and continuous establishment of higher performance’ standards. Around the 80s it became the dominant business paradigm of Japanese’ industries, with particular reference to Toyota (i.e., Toyota Production System, Toyotism). …but even less known is the fact that the Kaizen’s culture in not a fully Japan-made product. An introduction to Quality Assurance – DEMING Click to read

The DEMING Model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Formative Evaluation |
Summative Evaluation |
| Step by step evaluation of processes and day-by-day assessment of your activities |
Upon conclusion of any major result, look back at what has been done and try to compare it with your foreseen standards / expectations. |

Keywords
Quality Assurance, DEMING cycle, risk identification, risk assessment, monitoring, evaluation, management
Objectives/goals:The objective of this module is to nurture in readers a renewed awareness on the strategic role of (cyber) risk management for micro and small-medium enterprises operating within an interconnected digital ecosystem.
new agenda for risk management as a business functions that permeates transversely all task and activates while responding to the new urgent need of safeguarding businesses from cyber threats.
We will do that by sharing trustworthy, robust and reliable managerial frameworks that applies traditionally to all business functions.
Related training material


 Play Audio
Play Audio